Mechatronic and Control Development of a Virtual Metrology Frame Technique for Ultra Precision Machine Tools – Mr Jonathan Abir
This PhD project is focused on technologies that improve dynamic position control of a compact size machine tool. The research was made by design and development of a mechatronic system, which will be implemented in the compact size machine tool – µ4 made by Cranfield Precision Engineering Institute and Loxham Precision Ltd. This research is unique and contributes to knowledge by combining the apparent antagonistic requirements of a compact size machine tool with high dynamic performances. A novel mechatronic technique – virtual metrology frame, was developed alongside mechanical design approach, which optimises the requirements of the compact size machine tool and high dynamic performances requirements. Based on the developed technique, the expected machine performance is as if the machine has a metrology frame, without interfering with the size constraint.
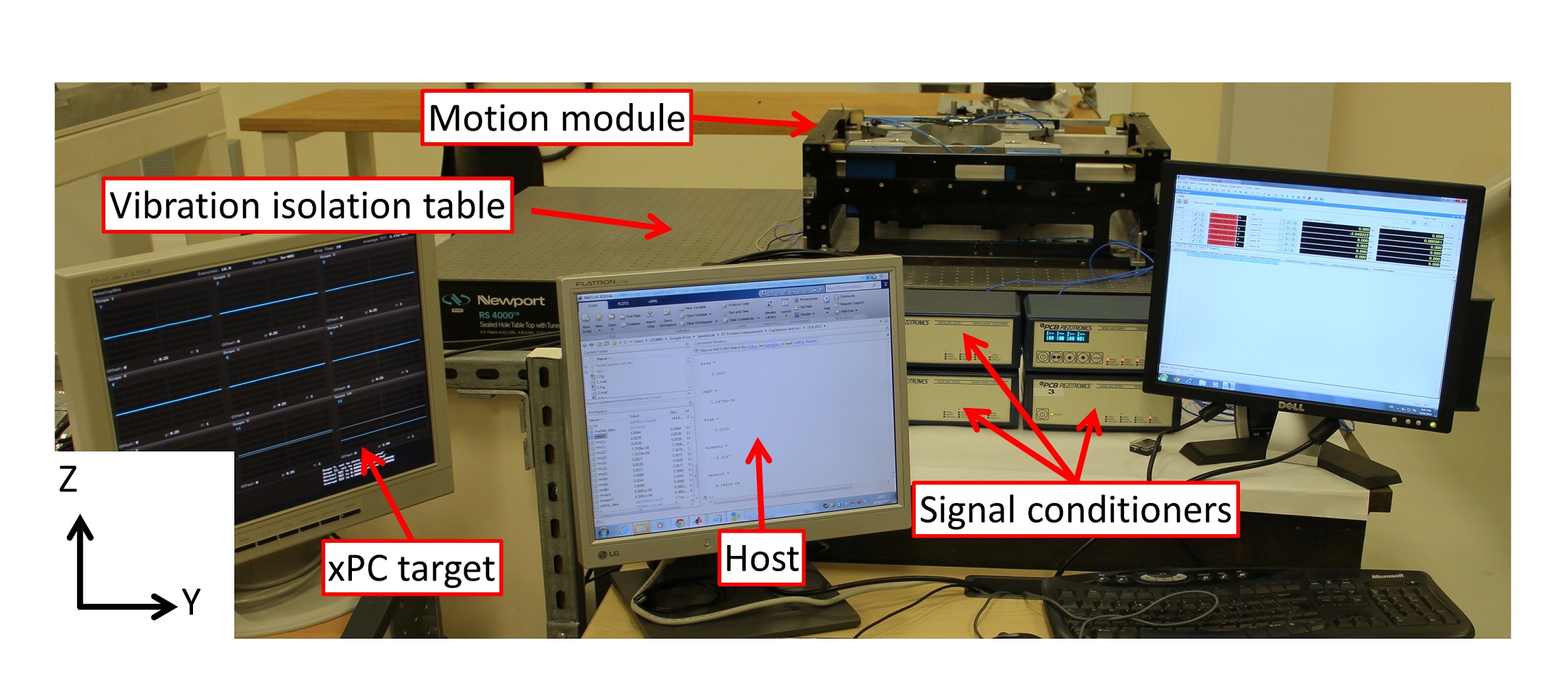
In this research, investigation and analysis of mechatronic designs were made as well as experimental work. To date, the experimental work includes system identification (using various techniques), thermal distortion measurements of linear motion module, and displacement based accelerometer measurements. Through the research, theoretical analysis and simulation were carried using Computer Aided Engineering software. Two main aspects of the research work were achieved:
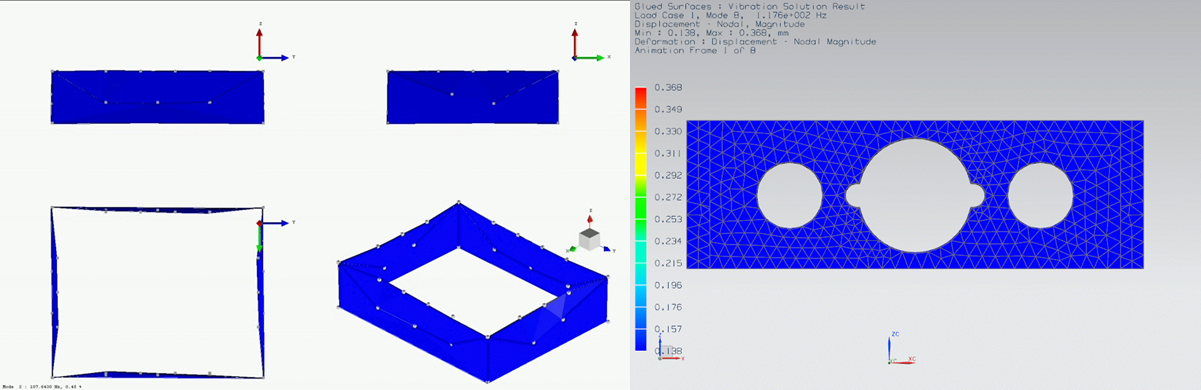
First, using experimental modal analysis, system identification and finite element simulation it was found that the significant dynamic effect, which influences the machine dynamic performances, is the flexible frame.
Second, a new technique was developed that acts as a virtual metrology frame. Having two different machine frames, metrology and force is common in high-end machine design, but due to the design constrains it hard to implement. Thus, accelerometers are used as supplementary information on the frame vibrations.
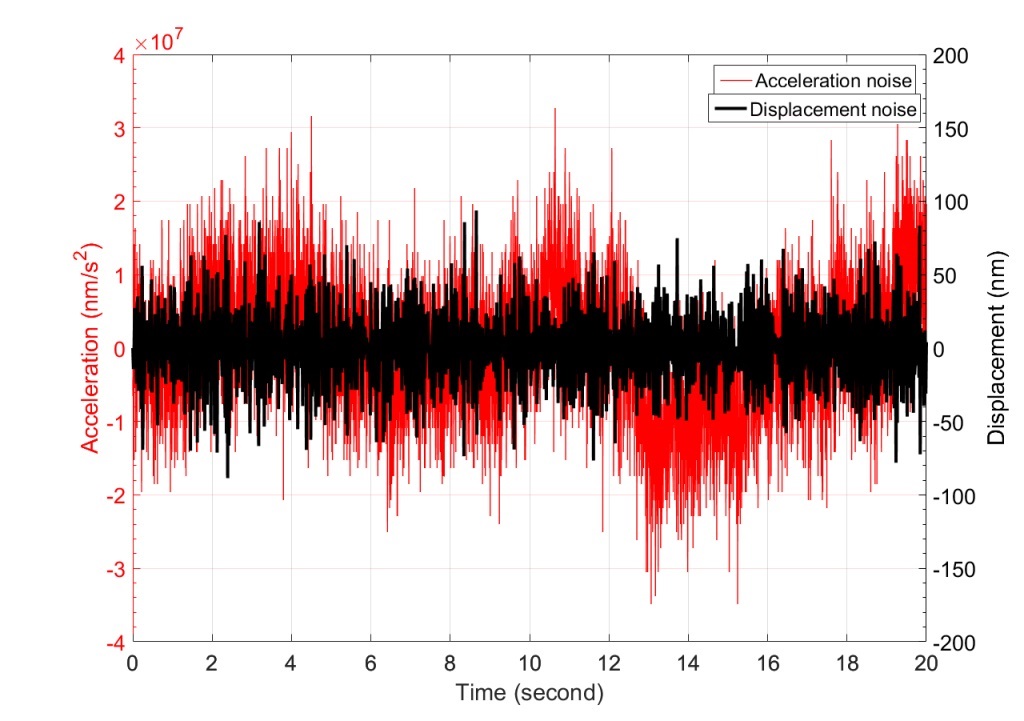
Long term integration (>10 s) of acceleration signals and high accuracy acceleration based displacement sensors has been largely unsuccessful. However, in this work a mechatronic system of a real-time, long term (>10 s), and accurate (σ< 30 nanometre) displacement estimator based on accelerometer was achieved.
The next step will be assessing the improvement to the machine performance by the developed solution. Then, improvements and extensions of that technique will be carried by optimising and automating the signal processing techniques alongside multiple axes demonstrator.
Outputs
Journal Publications
Abir, J., Longo, S., Morantz, P. and Shore, P. (2016). Optimized estimator for real-time dynamic displacement measurement using accelerometers, Mechatronics, 39, 1-11.
Conference Presentations
Abir, J., Longo, S., Morantz, P. and Shore, P. (2016). A novel accelerometer based feedback concept for improving machine dynamic performance, 7th IFAC Symposium on Mechatronic Systems, 5-8 September 2016, Loughborough University, Loughborough, UK.
Abir, J., Morantz, P., Longo, S. and Shore, P. (2016). An accelerometer based feedback technique for improving dynamic performance of a machine tool, Proceedings of the 16th International Conference of the European Society for Precision Engineering and Nanotechnology, 30 May-3 June 2016, University of Nottingham, Nottingham, UK.
Abir, J., Longo, S., Morantz, P. and Shore, P. (2016). Feedback based technique for improving dynamic performance of a small machine tool, American Society for Precision Engineering 2016 Spring Topical Meeting: Precision Mechatronic System Design and Control, 20-22 April 2016, Cambridge, MA, USA.
Abir, J., Morantz, P. and Shore, P. (2015). Position errors due to structural flexible modes, Poster presentation at euspen‘s 15th International Conference and Exhibition, 1-5 June 2015, Leuven, Belgium.
Abir, J., Shore, P and Morantz, P. (2015). Influence of temperature changes on a linear motion system, 11th International Conference on Laser Metrology, Machine Tool, CMM and Robotics Performance (LAMDAMAP 2015), 17-18 March 2015, University of Huddersfield, UK.
Abir, J., Morantz, P. and Shore, P. (2014). Design and control of a compact ultra-precision machine for high dynamic performance, 12th International Conference on Manufacturing Research (ICMR 2014), 9-11 September 2014, Southampton, UK.
Conference Publications
Abir, J., Longo, S., Morantz, P. and Shore, P. (2016). A novel accelerometer based feedback concept for improving machine dynamic performance, Proceedings of the 7th IFAC Symposium on Mechatronic Systems, 5-8 September 2016, Loughborough University, Loughborough, UK, 553-558.
Abir, J., Morantz, P., Longo, S. and Shore, P. (2016). An accelerometer based feedback technique for improving dynamic performance of a machine tool, Proceedings of the 16th International Conference of the European Society for Precision Engineering and Nanotechnology, 30 May-3 June 2016, University of Nottingham, Nottingham, UK, 197-198.
Abir, J., Shore, P and Morantz, P. (2015). Influence of temperature changes on a linear motion system, 11th International Conference on Laser Metrology, Machine Tool, CMM and Robotics Performance (LAMDAMAP 2015), 17-18 March 2015, University of Huddersfield, UK, 130-139.
Abir, J., Morantz, P. and Shore, P. (2015). Position errors due to structural flexible modes, Proceedings of the 15th International Conference of the European Society for Precision Engineering and Nanotechnology, 1-5 June 2015, Leuven, Belgium, 219-220.
Abir, J., Morantz, P. and Shore, P. (2014). Bottom-up modal analysis of a small size machine tool, Proceedings of the 3rd Annual EPSRC Manufacturing the Future Conference, 23-24 September 2014, Glasgow, UK, 147.
Abir, J., Morantz, P. and Shore, P. (2014). System identification of a small size machine, Proceedings of the 12th International Conference on Manufacturing Research (ICMR 2014), 9-11 September 2014, Southampton, UK, 35-40.
Digital Media
Abir, J. (2016). Novel technique improves speed and accuracy of micrometre scale precision CNC machine by 40%, User story published online at Speedgoat.ch
Abir, J. (2015). Design and control of a compact ultra precision machine tool for high dynamic performances, PhD project video produced for an informal Centre competition in 2015.
Posters
Abir, J., Morantz, P., Longo, S. and Shore, P. (2016). Design and control of a compact ultra-precision machine for high dynamic performance, EPSRC Centre for Innovative Manufacturing in Ultra Precision Steering Meeting Committee, 24 February 2016, Cranfield University, UK.
Abir, J., Morantz, P. and Shore, P. (2014). Bottom-up modal analysis of a small size machine tool, 3rd Annual EPSRC Manufacturing the Future Conference, 23-24 September 2014, Glasgow, UK.
Abir, J., Morantz, P. and Shore, P. (2014). Design and control of a compact ultra precision machine for high dynamic performance, EPSRC Centre for Innovative Manufacturing in Ultra Precision Mid Term Review, 20 May 2014, Cranfield University.